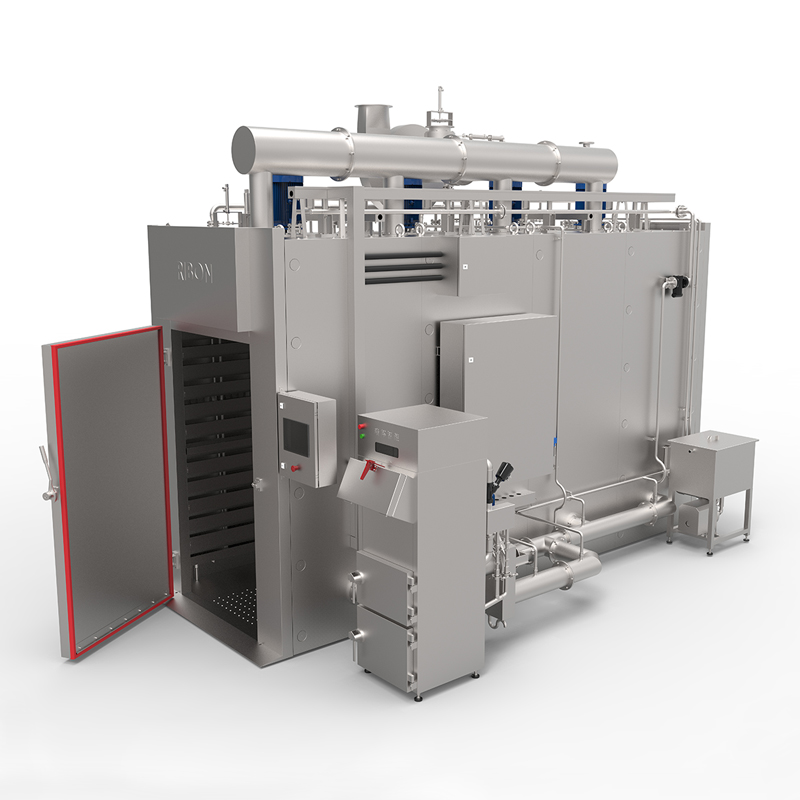
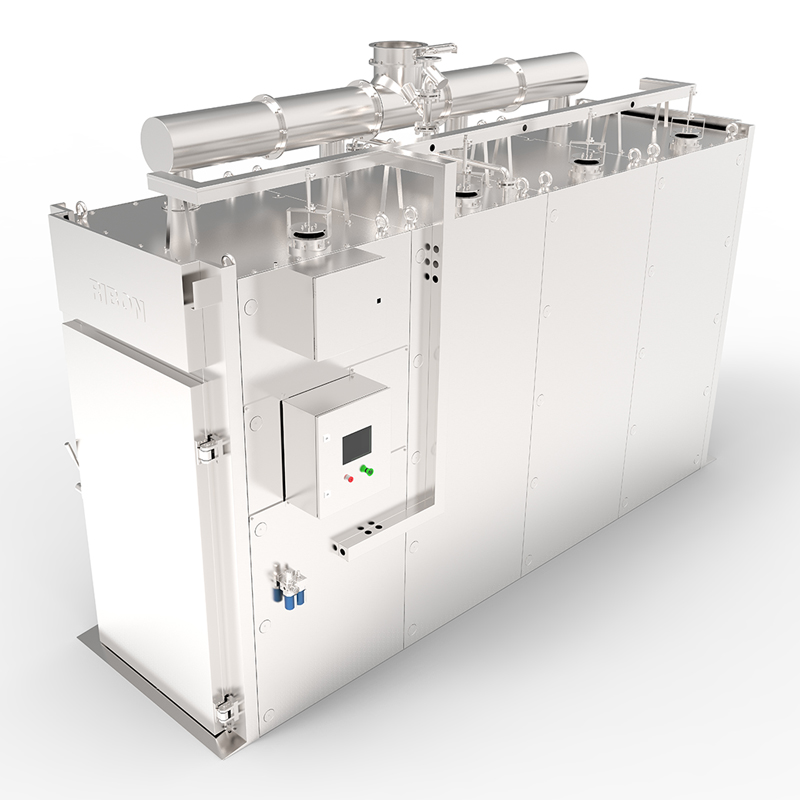
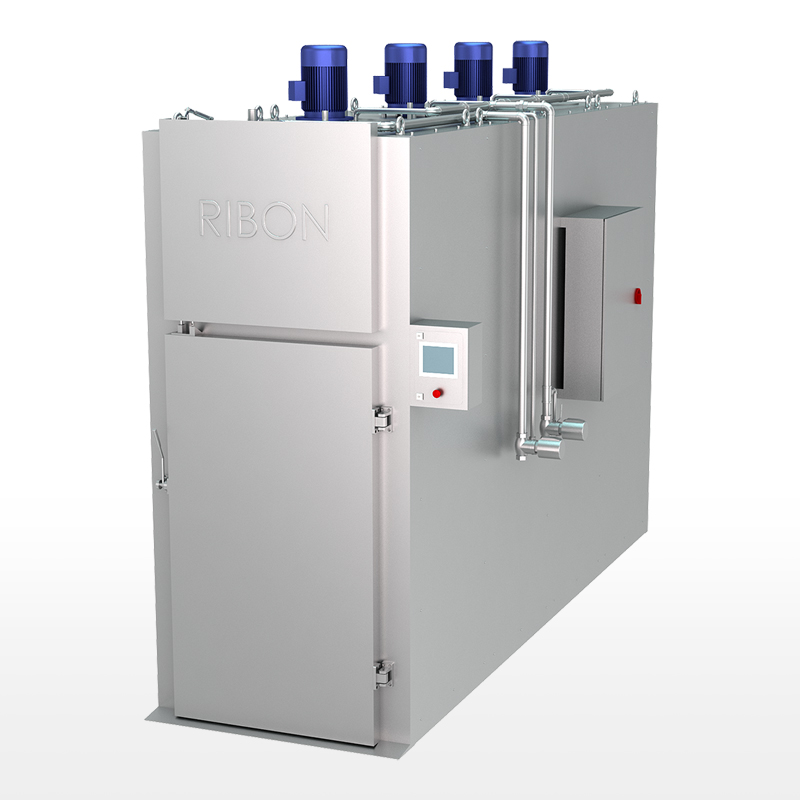
The process of transforming livestock into food products for human consumption is a complex and highly regulated industry. At its heart lies a range of specialized slaughtering equipment, designed to ensure efficiency, hygiene, safety, and humane treatment of animals. From small-scale artisanal operations to large industrial facilities, the right tools are paramount to a successful and ethical slaughtering process.
The Evolution of Slaughtering Technology
Historically, slaughtering was a labor-intensive and often unsanitary endeavor. However, advancements in engineering, materials science, and animal welfare understanding have revolutionized the industry. Modern slaughtering equipment is built with precision, utilizing materials like stainless steel for easy cleaning and durability, and incorporating automation to minimize human error and increase throughput.
Key Categories of Slaughtering Equipment
Slaughtering equipment can be broadly categorized based on the stages of the process:
Stunning Equipment: Humane stunning is the critical first step, rendering the animal unconscious before slaughter. This can involve:
Captive Bolt Guns: Used primarily for cattle, sheep, and goats, these devices deliver a percussive blow to the brain.
Electrical Stunning: Common for pigs and poultry, this involves applying an electric current to induce immediate unconsciousness.
CO2 Stunning Systems: Often used for pigs, these systems expose animals to a high concentration of carbon dioxide.
Hoisting and Conveying Systems: Once stunned, animals are typically hoisted for further processing. This includes:
Overhead Conveyors: Automated systems that move carcasses along the processing line.
Hoists and Gambrels: Used to lift and suspend carcasses for bleeding and evisceration.
Bleeding Equipment: Efficient bleeding is crucial for meat quality and hygiene. This often involves:
Bleeding Cones (for poultry): Devices that hold birds inverted for efficient blood collection.
Bleeding Rails: Areas designed to collect blood from larger animals.
Dehiding/Defeathering Equipment:
Hide Pullers: Mechanical systems that efficiently remove the hide from cattle.
Scalders and Defeathering Machines (for poultry): Scalders loosen feathers, which are then removed by rotating rubber "fingers" in defeathering machines.
Evisceration Equipment: This stage involves the removal of internal organs. Depending on the animal, this can range from manual evisceration tools to highly automated carousels and specialized machinery.
Splitting Saws: Used to halve carcasses (e.g., cattle, pigs) for easier handling and further processing.
Washing and Sterilization Equipment: Maintaining hygiene is paramount. This includes high-pressure washers, sterilization cabinets for tools, and automated carcass washing systems.
Processing and Deboning Equipment: While not strictly "slaughtering," this often follows immediately and includes saws, knives, and specialized machinery for breaking down carcasses into primal cuts and deboning.
Importance of Quality and Maintenance
The effectiveness and safety of a slaughtering operation are directly linked to the quality and maintenance of its equipment. Regular cleaning, sterilization, and preventative maintenance are essential to:
Ensure Food Safety: Preventing contamination and the spread of pathogens.
Maximize Efficiency: Reducing downtime and optimizing throughput.
Promote Animal Welfare: Ensuring equipment functions correctly for humane stunning and handling.
Extend Equipment Lifespan: Protecting investments and reducing replacement costs.
Comply with Regulations: Adhering to strict industry standards and government regulations.
The Future of Slaughtering Equipment
The industry continues to evolve, with ongoing research and development focusing on:
Increased Automation and Robotics: Further reducing manual labor and increasing precision.
Enhanced Sensor Technology: For real-time monitoring of animal welfare and meat quality.
Sustainable Practices: Developing more energy-efficient equipment and waste reduction technologies.
Improved Biosecurity Measures: Designing equipment that further minimizes the risk of contamination.
In conclusion, slaughtering equipment is far more than just a collection of tools; it is the backbone of a vital industry. Its design, operation, and maintenance are critical for producing safe, high-quality food products while upholding the highest standards of animal welfare and operational efficiency. As technology advances, the equipment used in slaughterhouses will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of meat production.






 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى