The Meat Slaughtering Line, a term that might sound a bit cold and industrial, is the very link connecting the farm to our dinner plates. It’s a highly integrated, sophisticated mechanical system designed to efficiently, hygienically, and humanely transform livestock into meat products fit for consumption. This is not just a simple production line; it’s a complex discipline that fuses animal science, food engineering, mechanical automation, and food safety management.
Automation and Efficiency: The Core of a Modern Slaughtering Line
In the past, slaughtering was a labor-intensive and inefficient process. Modern Meat Slaughtering Lines, however, have completely changed this by introducing automation. From the receiving and stunning of livestock to bleeding, skinning, evisceration, and finally, cutting, chilling, and packaging, every step is meticulously designed.
- Humane Stunning: Modern slaughtering lines prioritize humane treatment. Livestock is quickly and painlessly stunned using methods like electrical stunning or carbon dioxide gas, ensuring the animals enter the next phase without suffering. This not only respects animal welfare but is also crucial for meat quality, as stress can negatively impact its texture and flavor.
- Precise Bleeding and Skinning: Automated equipment ensures the bleeding process is quick and thorough, which is vital for the meat’s shelf life. Subsequently, mechanical skinners replace manual labor, increasing efficiency and preventing secondary contamination of the carcass.
- Fine-tuned Cutting and Standardization: Traditional slaughtering often relied on the butcher’s experience. On a Meat Slaughtering Line, however, the carcass is transported to different stations where specialized cutting equipment follows pre-set programs for precise segmentation. This not only boosts production efficiency but also ensures that every cut of meat meets market standards for size and weight.
Food Safety: The Lifeline of the Slaughtering Line
Of all the considerations for a Meat Slaughtering Line, food safety is undoubtedly the most critical. Every step must strictly adhere to hygiene standards to prevent microbial contamination.
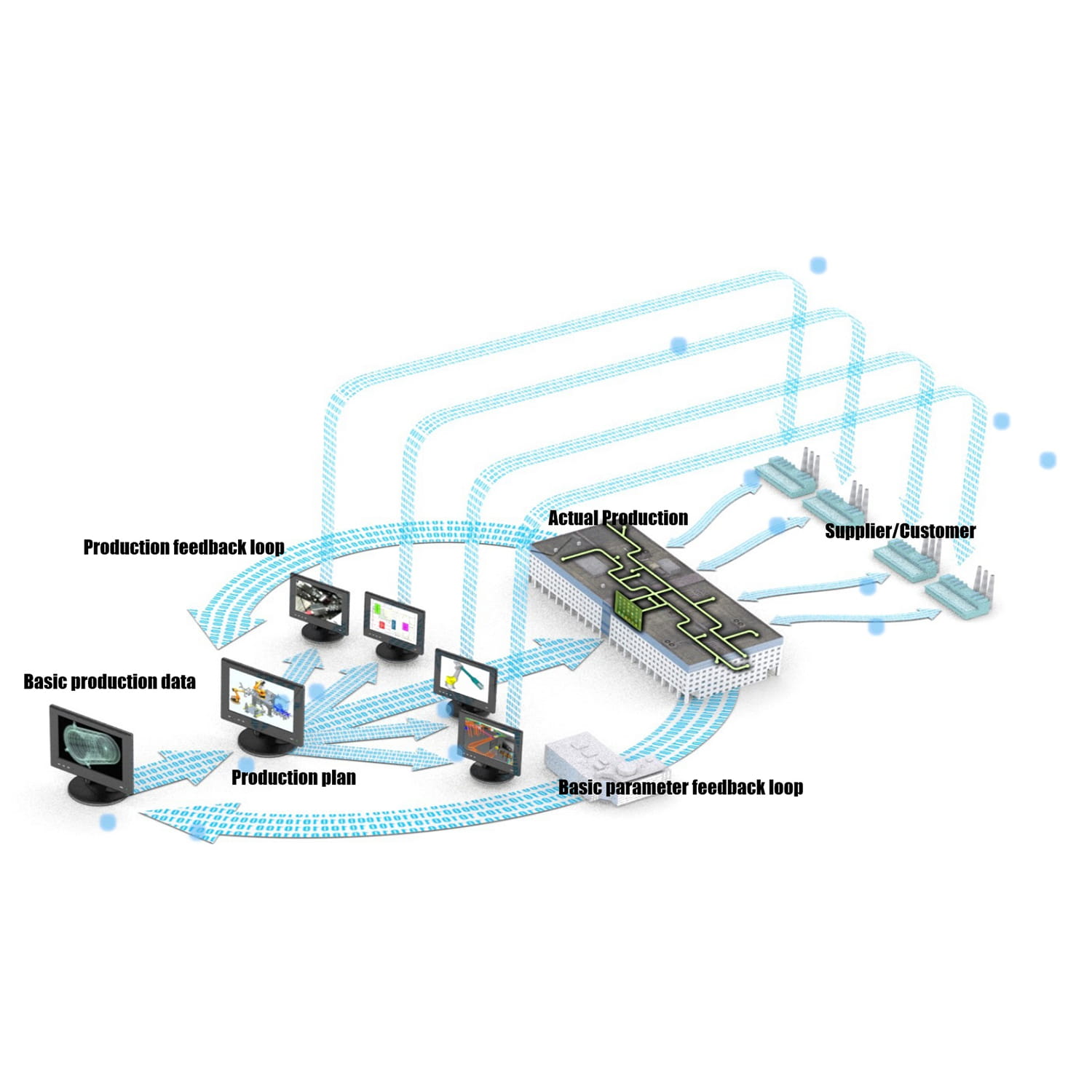
- Full Monitoring and Traceability: Modern slaughtering lines are typically equipped with advanced monitoring systems that record the production process in real-time. Every batch of meat can be traced back to its origin, including farm information, slaughter date, and processing details. This transparency is not just a promise to consumers but also a powerful tool for government regulation.
- Rigorous Hygiene and Disinfection: All equipment and tools on the slaughtering line must undergo regular, high-intensity disinfection. High-temperature steam, ultraviolet light, and chemical disinfectants are widely used for cleaning. Workers must also wear sterile clothing and strictly follow hygiene protocols.
- Rapid Chilling and Cold Chain: After slaughter, the carcass must be quickly moved to a chilling room to lower its core temperature to a safe range, inhibiting bacterial growth. The meat products then enter refrigeration or freezing stages, and are transported to retail outlets through a complete cold chain system to ensure their freshness.
Sustainability and Future Trends
Future Meat Slaughtering Lines will focus even more on sustainability. This includes reducing water and energy consumption and effectively utilizing by-products. For example, bones, blood, and offal can be processed into animal feed, biofuels, or pharmaceutical raw materials, enabling resource recycling and maximizing the value of the livestock.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning will make the slaughtering line even “smarter.” Machine vision can automatically identify defects in the carcass for precise classification, while predictive maintenance systems can warn of equipment failures in advance, reducing downtime.
The Meat Slaughtering Line is more than just a production line; it’s a complex system that integrates multi-disciplinary knowledge and high levels of automation. Its existence ensures we can obtain high-quality meat products efficiently, safely, and humanely, making it an indispensable part of the modern food industry.





 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى